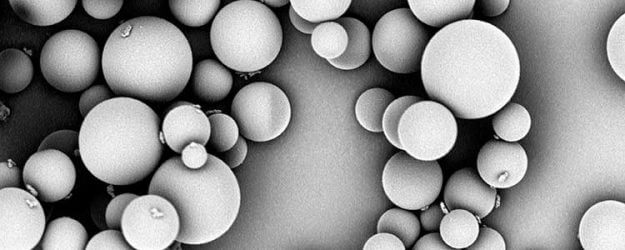
AVEKA's Prilling/Melt Spraying capabilities can turn solid materials into fine, free-flowing powders with a tight particle size distribution.

What is Prilling?
Prilling, also known as Melt Spraying, is a continuous process of atomizing molten liquids or mixtures and cooling the resulting droplets to create a spherical powder. Suitable materials for processing generally are solids at room temperature, stable in a molten state with relatively low viscosity and have a low melt temperature. A typical material used in this process is wax. Other commonly used terms for prilling are Spray Congealing, Spray Chilling, Melt Atomization and Micronization.
For Melt Spraying, the molten material is atomized using a two-fluid nozzle inside a vertical chamber. The atomization air can be heated up to 520°C. The resulting product is a fine, free-flowing powder typically with particle sizes less than 100 microns. The final product is screened directly off of the collection cyclone to remove any large chunks of wax. The material can also be screened to the customer’s desired particle size specification. Any material that is too small or too large can be reprocessed. The final product is packaged into double-lined fiber drums or a container that fits the customer’s needs. Melt Sprayed materials are used in many industries, but a common use is in metal casting industries as a lubrication.
AVEKA’s full-service analytical laboratory allows for rapid process adjustments during trials and excellent quality control for production operations. For example, melt sprayed products can be characterized by imaging particle morphology and measuring particle size distribution. Additionally, extensive pre- and post-processing capabilities contribute to the turnkey experience AVEKA provides.